The cellular modifier MOAG‐4/SERF drives amyloid formation through charge complementation | The EMBO Journal
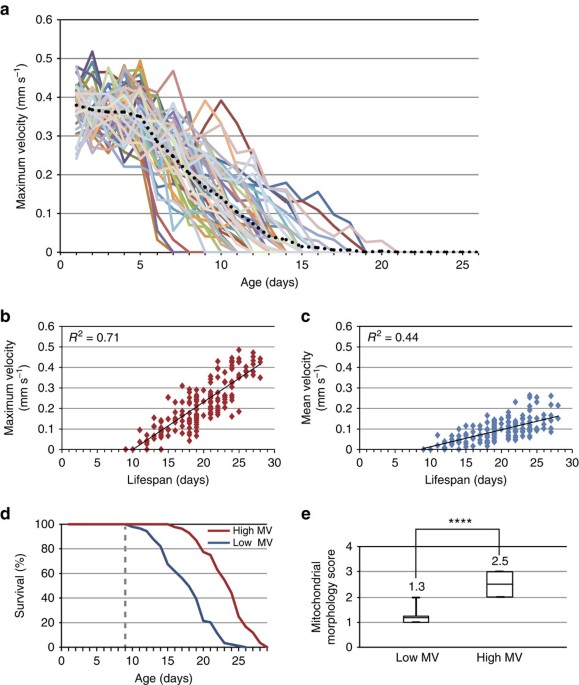
C. elegans maximum velocity correlates with healthspan and is maintained in worms with an insulin receptor mutation | Nature Communications
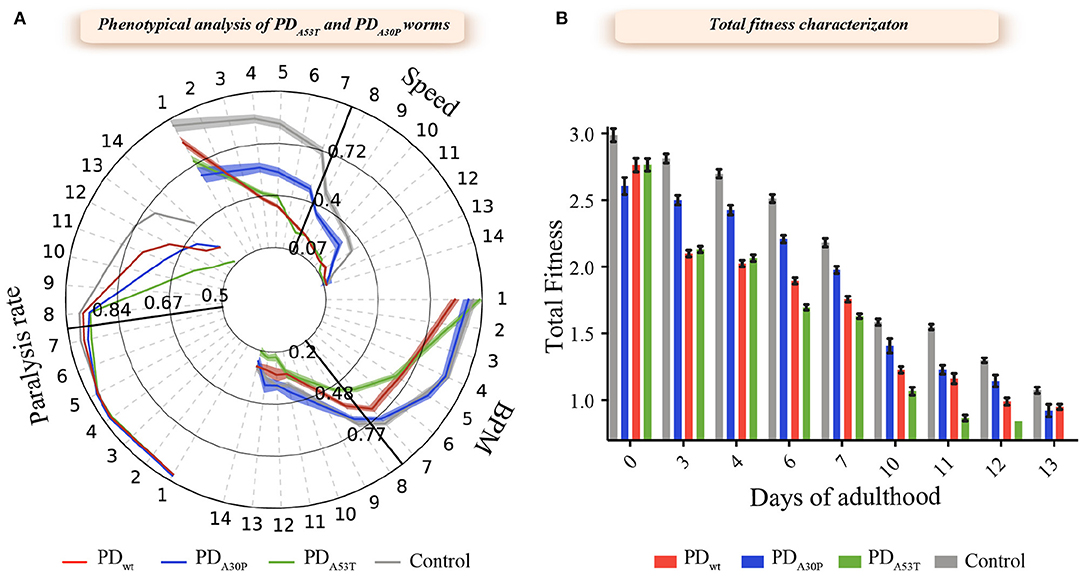
Frontiers | Comparative Studies in the A30P and A53T α-Synuclein C. elegans Strains to Investigate the Molecular Origins of Parkinson's Disease | Cell and Developmental Biology

Protective role of DNJ-27/ERdj5 in Caenorhabditis elegans models of human neurodegenerative diseases. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Protective role of DNJ-27/ERdj5 in Caenorhabditis elegans models of human neurodegenerative diseases. - Abstract - Europe PMC
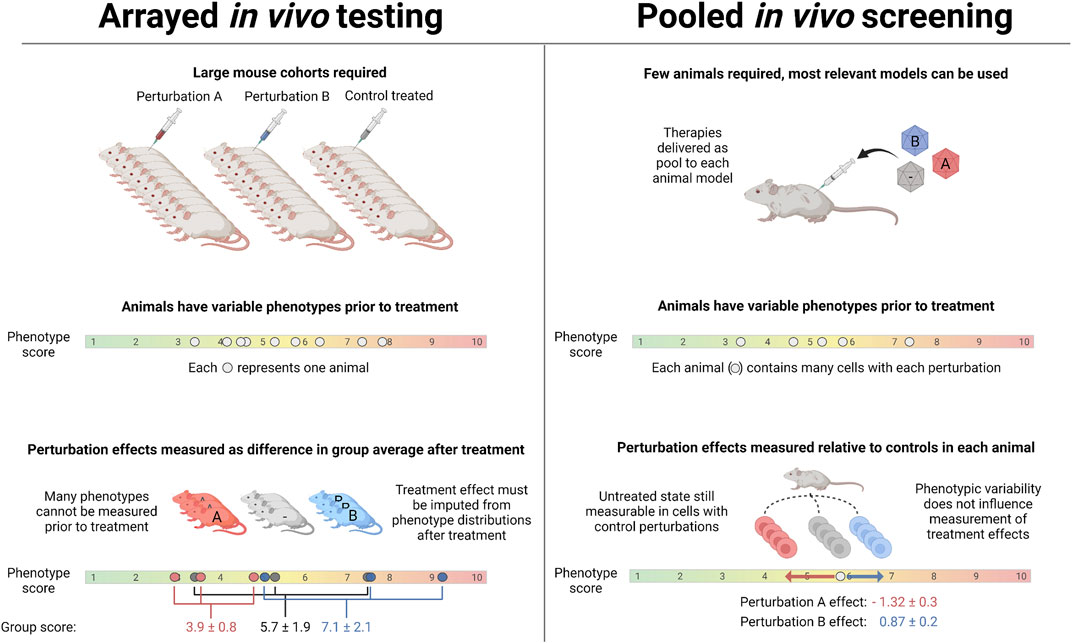
Frontiers | In vivo Pooled Screening: A Scalable Tool to Study the Complexity of Aging and Age-Related Disease | Aging
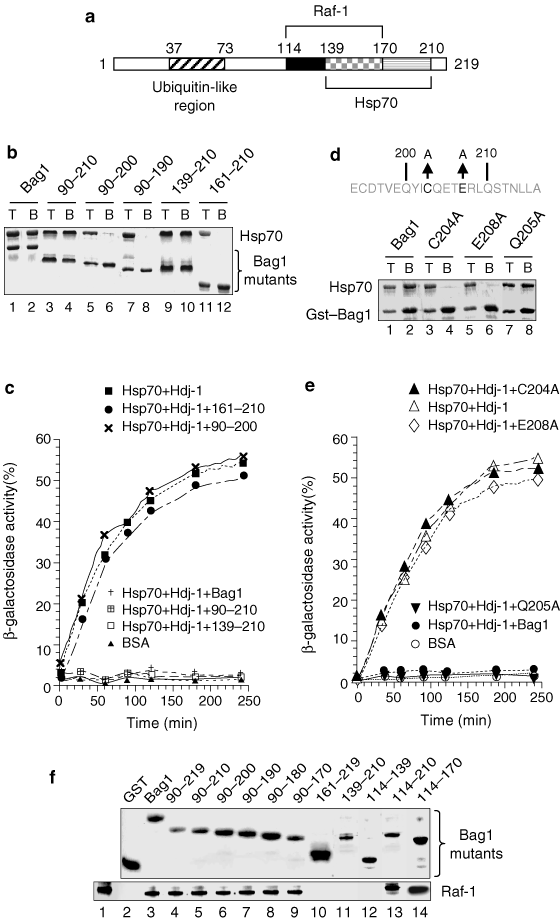
Bag1–Hsp70 mediates a physiological stress signalling pathway that regulates Raf-1/ERK and cell growth | Nature Cell Biology
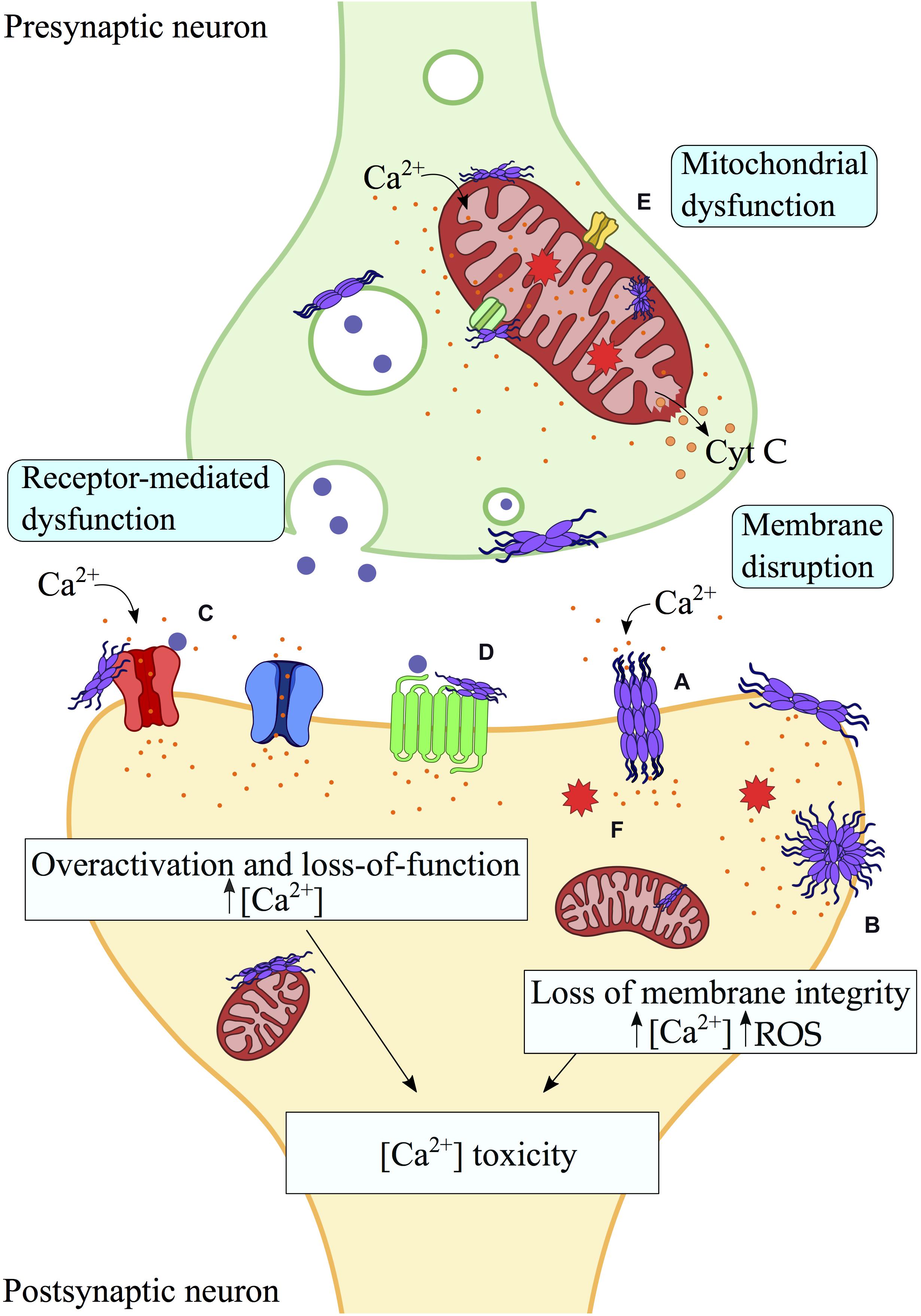
Frontiers | Membrane Interactions and Toxicity by Misfolded Protein Oligomers | Cell and Developmental Biology

The cellular modifier MOAG‐4/SERF drives amyloid formation through charge complementation | The EMBO Journal

Frontiers | A Novel Hybrid Model for Drawing Trace Reconstruction from Multichannel Surface Electromyographic Activity | Neuroscience

Genome-wide RNA interference screen identifies previously undescribed regulators of polyglutamine aggregation | PNAS

Age‐ and disease‐specific changes of the kynurenine pathway in Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease - Sorgdrager - 2019 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library

The cellular modifier MOAG‐4/SERF drives amyloid formation through charge complementation | The EMBO Journal

Kinetic analysis reveals that independent nucleation events determine the progression of polyglutamine aggregation in C. elegans | PNAS

Identification of an evolutionary conserved structural loop that is required for the enzymatic and biological function of tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase | Scientific Reports

Protective role of DNJ-27/ERdj5 in Caenorhabditis elegans models of human neurodegenerative diseases. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Protective role of DNJ-27/ERdj5 in Caenorhabditis elegans models of human neurodegenerative diseases. - Abstract - Europe PMC

The cellular modifier MOAG‐4/SERF drives amyloid formation through charge complementation | The EMBO Journal